Based on Google’s recently released on their AI Agent Security article from a CISO perspective…
AI Agent Security Guidelines
- Agents must have well-defined human controllers: Agents must operate under clear human oversight, with the ability to distinguish authorized user instructions from other inputs.
- Agent powers must have limitations: Agent actions and resource access must be carefully limited and dynamically aligned with their intended purpose and user risk tolerance. This emphasizes the least-privilege principle.
- Agent actions and planning must be observable: Agent activities must be transparent and auditable through robust logging and clear action characterization.
Google’s Suggested Approach
Google advocates for two distinct layers:
- Layer 1: Use traditional, deterministic measures, such as runtime policy enforcement. Runtime policy engines act as external guardrails, monitoring and controlling agent actions before execution based on predefined rules. These engines use action manifests to capture the security properties of agent actions, such as dependency types, effects, authentication, and data types.
- Layer 2: Deploy reasoning-based defense strategies. This layer uses the AI model’s own reasoning to enhance security. Techniques such as adversarial training and using specialized models as security analysts can help the agent distinguish legitimate commands from malicious ones, making it more resilient against attacks, data theft, and even model theft.
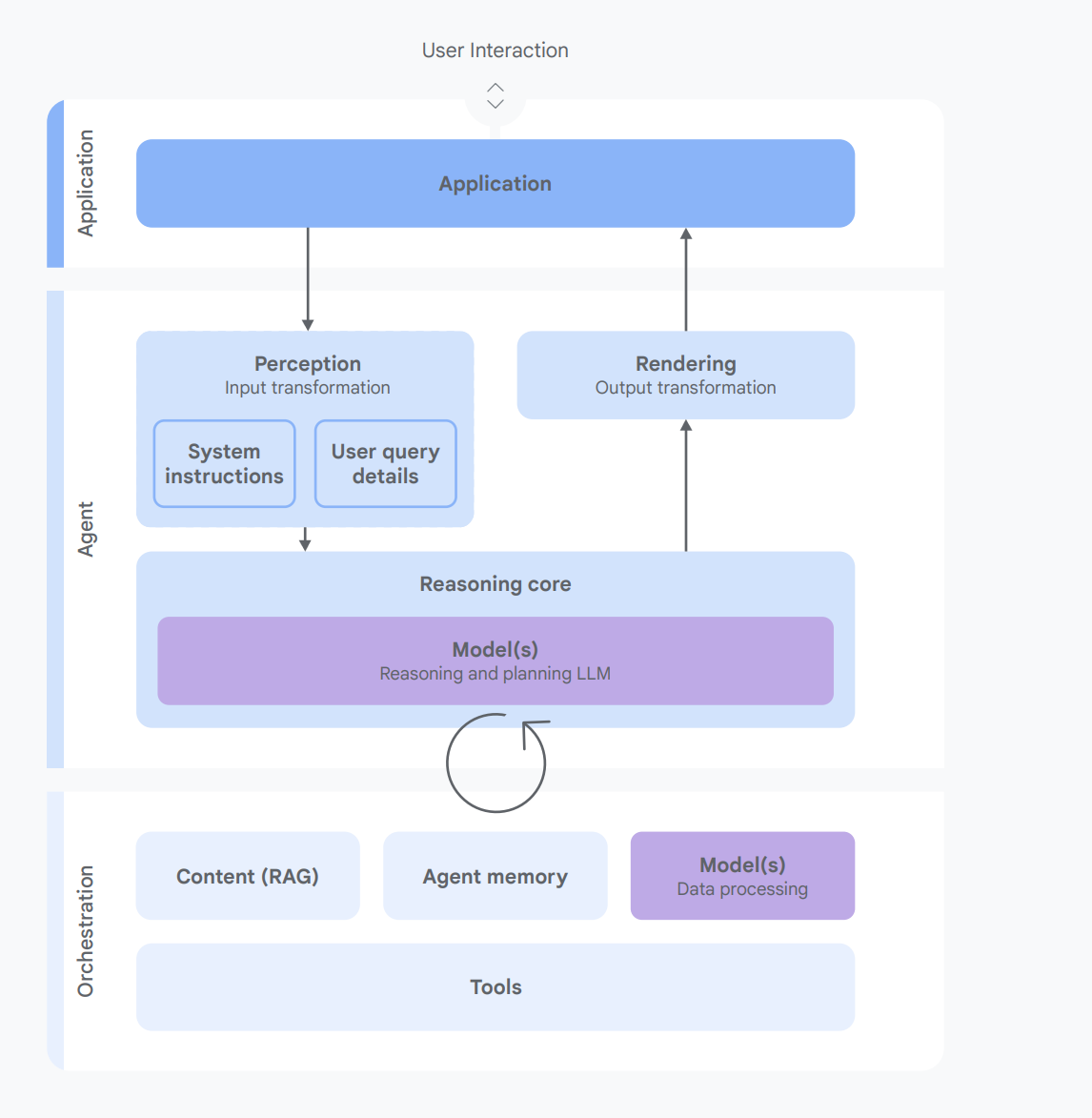
Initial Base AI Agent Concept
Key Security Risks
Risk 1: Rogue Actions
Summary: This is when an AI agent performs harmful or unintended actions. This can happen because it is tricked by malicious instructions hidden in data (like an email or website) or because it misunderstands ambiguous user commands or misinterprets how to use an external tool.
Risk 2: Sensitive Data Disclosure
Summary: This is when an AI agent improperly reveals private information. Attackers can achieve this by tricking the agent into sending data to an external location (e.g., in a URL) or by manipulating its response to include the sensitive data directly.
Core principles for AI Agent security
Now here’s how Google advises on risk mitigation…
Principle 1: Human Oversight and Control
- Statement: Every AI agent must be clearly linked to a human controller, who must approve any critical or irreversible actions, ensuring the system can always distinguish between the user’s commands and other data.
Principle 2: Limited and Purpose-Aligned Powers
- Statement: An agent’s abilities must be strictly limited to its intended purpose, with permissions dynamically adjusted for each specific task, and users must always be able to review and revoke its access.
Principle 3: Observability and Transparency
- Statement: All agent actions and reasoning steps must be securely logged and made observable, with a user interface that provides clear insight into the agent’s thought process to build trust and allow for security audits.
Reference
https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/identity-security/cloud-ciso-perspectives-how-google-secures-ai-agents
https://storage.googleapis.com/gweb-research2023-media/pubtools/1018686.pdf
Source Credit: https://medium.com/google-cloud/google-ai-agent-security-82254a923432?source=rss—-e52cf94d98af—4




